A customer portal is a secure website where customers can log in to view and manage support tickets, access a knowledge base, and update their account information. It also lets them engage with a brand on their own terms. In short, a customer portal acts as a retention and growth engine, reducing friction, building trust, and keeping customers connected.
The best portals combine clear visibility, intuitive design, and smart integration with the CRM. When done right, they turn support into a seamless experience and service into a competitive advantage.
This article examines and breaks down the features, setup, and tools that make that possible, starting with how a customer portal actually works.
Table of Contents
- What is a customer portal?
- Customer Portal Features That Matter Most
- Best Customer Portal Tools
- How to Set Up Your Customer Portal (using HubSpot Service Hub)
- How to Choose Customer Portal Software That Fits Your Stack
- Customer Portal vs Client Portal vs. Sales Portal
- Frequently Asked Questions About Customer Portals
What is a customer portal?
A customer portal is a secure, self-service website where customers can track support tickets, find answers in a knowledge base, and manage their account details. It brings all customer interactions into one place, giving users more control and teams more visibility.
Because customer portals centralize communication and data, companies can use them to reduce friction, shorten resolution times, and build trust. Customers and businesses benefit from the increased transparency. Because they can see progress, access help anytime, and feel confident they’re being heard, service teams gain efficiency and enhance consistency.
Customer portals become even more powerful levers for retention and long-term growth when connected to a CRM. Smart data makes every interaction more personal, whether it’s surfacing relevant articles or prioritizing requests from key accounts.
Why customer portals help businesses retain customers:
- Improved Efficiency and Quality. Support teams can focus on higher-value interactions. This kind of visibility and responsiveness is especially critical in SaaS environments, where fast, proactive support directly impacts retention — learn more about SaaS customer support best practices.
- Enhanced Transparency. Customers gain visibility into ticket status and history, which means fewer churn triggers. For ecommerce businesses, a customer portal can double as an order-tracking hub and self-service center. Here’s how to create an excellent ecommerce customer service experience.
- Deepened Relationships. Connecting customer portals to CRM data yields a higher degree of personalization with content that meets customer needs and interests.
- Heightened Integration. When customers are able to get self-service access to necessary information, they adopt and fully integrate the solutions, making switching harder.
Customer Portal Features That Matter Most
Certain customer portal features matter most when it comes to reducing friction, improving transparency, and building long-term trust. The best portals balance secure access, intuitive self-service, and clear visibility into every request. A customer portal enables ticket creation, status tracking, and knowledge base access.
Service reps consistently point to the following must-have features when evaluating customer portal software:
- Authentication and access control (SSO/MFA). Secure logins protect customer data and limit access to authorized users.
- Ticket creation and status tracking. Customers can submit requests, see progress in real time, and reply directly within the portal.
- Knowledge base and federated search. A searchable help center helps users find answers quickly and deflects common tickets. A strong knowledge base helps customers self-solve quickly and reduces ticket volume — a core part of any web self-service strategy.
- Case deflection with forms, chat, or AI guidance. Smart routing and automated suggestions reduce workload for support teams.
- Account and document management. Let customers update profiles, download invoices, and view order history from one dashboard.
- Feedback and community tools. Customer feedback portal features allow customer service teams to embed surveys or discussion forums to capture insights and build loyalty.
- Multilingual and multi-brand support. Serve global customers with localized content and brand-specific portals.
- Mobile-friendly UX and accessibility. Ensure every user can access help on any device, regardless of ability.
- Analytics and reporting. Track ticket deflection, satisfaction scores, and portal engagement to measure impact.
Each feature plays a role in creating a consistent, transparent experience. Together, these features turn customer portals into a retention engine that scales support while keeping service personal.
HubSpot Service Hub offers a CRM-native customer portal, knowledge base, and help desk.
Pro tip: When choosing or configuring a customer portal, look first at features that solve customers’ biggest friction points. For example, if clients often ask, “Where’s my ticket?” focus on ticket visibility and status tracking before adding advanced AI or multilingual support.
Best Customer Portal Tools
The right customer portal software connects customers, data, and service teams in one seamless experience. Below are five leading options for growing businesses — starting with HubSpot Service Hub.
1. HubSpot Service Hub
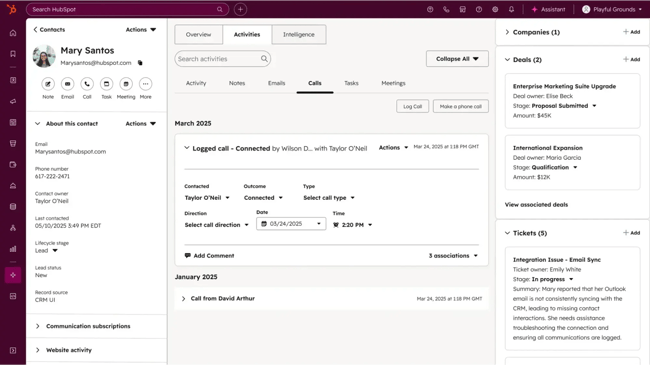
HubSpot Service Hub includes a CRM-native customer portal built directly on the HubSpot Smart CRM. It lets customers view and reply to ticket updates, access the company knowledge base, and gives service teams a unified view of every customer interaction.
What I like: Smart CRM provides unified customer data for personalized portal experiences. Support teams can show relevant articles, trigger workflows from ticket events, and segment customers into access groups, taking the portal beyond a help desk to become a true retention tool.
Best for: Growing businesses using (or planning to use) the HubSpot ecosystem across Marketing, Sales, and Service.
Pricing: Customer portal is included in the Professional Plan ($90 per seat/month) and the Enterprise Plan ($150 per seat/month).
Pro tip: Start with self-service and ticket-deflection features first, then layer in AI guidance and account-based workflows as adoption grows.
2. Zendesk
Zendesk’s customer portal provides centralized ticket tracking, a robust knowledge base, and built-in community forums. It’s a trusted option for service teams that handle large ticket volumes.
What I like: Scalable, enterprise-ready tools with strong analytics and multi-brand support.
Best for: Mid-size to large organizations managing high support volume or multiple brands.
Pricing: Plans including a customer portal start at $115 per agent/month for the Suite Professional Plan.
Pro tip: Optimize Zendesk’s branding and user interface early for a cohesive, on-brand experience that drives faster adoption and higher CSAT scores.
3. Salesforce Experience Cloud
Salesforce Experience Cloud powers customer self-service portals tightly integrated with Salesforce CRM. It connects support, data, and automation in one platform.
What I like: Highly customizable and scalable for enterprise workflows and multi-department teams.
Best for: Enterprises already using Salesforce that need deep integration and configurability.
Pricing: Authenticated Portals and Customer Communities require an existing Salesforce ServiceCloud account. Some plans include them, others start at $2 a month per login.
Pro tip: Leverage automation to route cases and surface relevant content for logged-in users. These small efficiencies add up fast at enterprise scale.
4. Zoho Desk
Zoho Desk offers a lightweight, affordable customer portal designed for fast setup and flexible integration with Zoho CRM.
What I like: The ASAP Self Service portal features simple configuration, strong value, and a clean user interface ideal for small teams.
Best for: Small to midsize businesses seeking a budget-friendly service solution.
Pricing: Plans with the ASAP self-service portal start at $14 per user/month for the Standard plan.
Pro tip: Pair Zoho’s portal with its built-in AI assistant, Zia (available at the Enterprise level), to automate ticket triage and improve response times.
5. Clinked
Clinked is a secure client and customer portal focused on collaboration and document sharing rather than ticketing. It’s ideal for firms managing ongoing client relationships.
What I like: Secure file sharing, project visibility, and customizable workspaces.
Best for: Professional services, legal, and financial teams that prioritize document management and client collaboration.
Pricing: Starts as low as $95/month for the Lite Plan.
Pro tip: Use Clinked to centralize client files and feedback loops — it reduces email clutter and keeps communication auditable.
Whichever tool you choose, prioritize CRM integration. A portal connected to your CRM ensures every service interaction feeds customer data back into your broader relationship strategy — making support more personal and retention-focused.
How to Set Up Your Customer Portal (Using HubSpot Service Hub)
Setting up a customer portal in HubSpot Service Hub is straightforward. The platform gives service teams full control over branding, permissions, and visibility, all within the existing CRM. Here’s how to do it.
1. Enable the customer portal. Go to Service → Settings → Customer Portal and toggle the feature on.
2. Customize branding. Ensure the logo, colors, and domain match the company website. Consistent branding builds trust and keeps the experience seamless.
3. Set access and authentication. Define who can log in and what they can see. Use SSO or MFA where possible. HubSpot lets leaders decide whether contacts can view only their tickets or all company tickets.
Note: As you set up authentication, keep your signup and login experience simple. A user-friendly registration process helps reduce login friction and boosts adoption.
4. Connect the knowledge base. Link help articles so customers can self-serve before submitting a ticket. Categories and tags make content easy to find.
5. Configure ticket pipelines and views. Choose which ticket stages appear in the portal, customize ticket fields, and decide how updates display to customers.
6. Add self-service and deflection tools. Use forms, chatbots, or AI suggestions to route requests efficiently. This step helps lower ticket volume and improve first-touch resolution.
7. Test internally. Run through the portal as both a customer and service agent. Be sure to check branding, ticket visibility, and notifications before launch.
8. Launch and promote. Announce the portal in support emails, help articles, and chat widgets. Include direct links wherever customers reach out for help. When the portal goes live, a “Portal Quick Start” document that covers how to submit tickets, view status, and access documents can improve customer adoption, which matters as much as functionality.
9. Monitor and improve. Track logins, ticket deflection rates, and satisfaction scores. From there, iterate to update the knowledge base and workflows based on real customer behavior.
[EMBED Video starting at the 10:12 mark: AI-Powered Customer Service | HubSpot Service Hub Walkthrough (2024)]
Pro tip: Start small. Launch your portal with a single ticket pipeline or customer segment, then expand once the service team and customers are comfortable. This phased approach builds adoption and reduces launch friction.
How to Choose Customer Portal Software That Fits Your Stack
A customer portal is only as strong as its fit within a company’s tech stack. The right customer portal software connects with the CRM, automates workflows, and unifies data across teams.
Use this checklist to guide the evaluation process:
- CRM integration and data alignment. Make sure the portal connects seamlessly with the company CRM. Every interaction should update contact records and help personalize future service.
- Knowledge base and search quality. Look for strong indexing and federated search that makes answers easy to find. A poor search experience creates more tickets.
- AI and automation capabilities. Choose tools that use AI to recommend articles, route tickets, and assist agents — with guardrails to maintain accuracy and tone.
- Security and compliance. Verify SSO, MFA, and encryption standards. For industries with strict regulations, confirm GDPR, SOC 2, or HIPAA compliance.
- Multilingual and multi-brand support. If you serve multiple regions or brands, ensure your portal supports localized content and brand-specific experiences.
- Admin UX and analytics. Check how easy it is to configure content, workflows, and reports. Portals with intuitive admin tools save hours each week.
- Ecosystem and support. Evaluate integrations, onboarding help, and vendor support quality.
- Scalability. Pick software that can grow with your customer base and product lines.
- Cost vs. value. Compare pricing models carefully. The best tool balances affordability with long-term ROI through automation and retention gains.
Pro tip: Before committing, map your customer journey and identify the highest-friction points. Then choose software that directly resolves those gaps, not just the tool with the longest feature list.
Customer Portal vs Client Portal vs Sales Portal
Each type of portal serves a different audience and purpose. A customer portal enables self-service support, a client portal facilitates collaboration and document sharing, and a sales portal empowers sales teams with deal and content management.
Portal Type | Primary User | Main Purpose | Typical Features |
Customer Portal | End customers (B2B or B2C) | Provides self-service, ticket tracking, and account visibility |
|
Client Portal | Clients of service-based businesses | Centralizes collaboration, project visibility, and document sharing |
|
Sales Portal | Internal sales teams and partners | Organizes deal assets, training, and content for sales enablement |
|
Frequently Asked Questions About Customer Portals
What should be on a customer portal homepage?
A customer portal homepage should show key actions and status at a glance:
- Open tickets.
- Recent updates.
- Easy access to “Submit a Request” or “Search Help” options.
Customer service teams launching customer portals should also include a knowledge base search bar, profile settings, and quick links to documents or order history. A simple, mobile-friendly design empowers users to find answers fast.
How do I decide which tickets customers can see?
Control visibility through access permissions in your portal settings. Most businesses let customers view tickets tied to their contact record, while B2B accounts often allow all company users to see shared tickets. Role-based access and SSO help to keep data secure and segmented.
When should I add AI agents to my portal?
Add AI once you have a strong knowledge base and clear ticket categories. AI agents work best when they can reference accurate content and detect patterns.
Start by using AI to suggest related articles or route tickets, then expand to conversational bots once you’ve validated accuracy. AI agents power personalized self-service and instant answers in customer portals.
Can a customer portal handle multiple brands or languages?
Yes. Most enterprise-grade portals support multilingual and multi-brand setups, letting you customize content, domains, and design per brand. HubSpot’s customer portal, for example, supports 40+ languages and brand-specific ticket pipelines.
How do I migrate from an email-only support model to a portal?
Start with an audit of current support workflows and FAQ data. Next, build a small knowledge base, enable ticket tracking, and launch the portal to a pilot group. Then, gradually direct customers to log in instead of emailing. Auto-replies and chat widgets can guide users toward the portal until adoption grows.
Pro tip: Focus on usability first. The easier the portal is to navigate, the faster your customers will switch from email to self-service — and the sooner your team sees the benefit.
How can I get started with a customer portal in 30 days?
Many companies are eager to dive in. Here’s a sample plan for getting started quickly.
- Week 1: Audit current support tickets + FAQs, pick your portal tool (e.g., Service Hub), define login domain/branding.
- Week 2: Build knowledge base articles, define ticket pipelines, set access rules, configure authentication (SSO/MFA), and set up group logic.
- Week 3: Set up the portal — customize UI, embed login link, connect CRM data, run internal tests with staff/customers, and refine.
- Week 4: Soft-launch with select customers, monitor metrics (login rate, ticket deflection, CSAT), train support team, promote portal, and move entirely off email-only for status updates.
By the end of 30 days, it’s possible to have a functioning customer care portal that delivers self-service and status transparency. Then you can iterate for advanced features like AI chat, multilingual support, and document workflows.
Turn your customer portal into a retention engine.
Companies implementing customer portals gain much more than “just” a help desk. By giving customers a secure self-service platform, ticket visibility, knowledge access, and account management, service teams can reduce friction, increase transparency, and strengthen customer loyalty.
Tools like HubSpot Service Hub empower service teams to build a CRM-native portal that ties service data to customer lifecycle metrics, delivering on metrics like measurable ROI, improved segment usage, and personalized experiences.
If customer service teams are ready to move from a reactive support model to one that’s more strategic, launching a customer portal is one of the highest ROI investments to consider.
Start your journey with the portal feature in Service Hub and turn your customer portal into a competitive advantage.
![]()

